Description
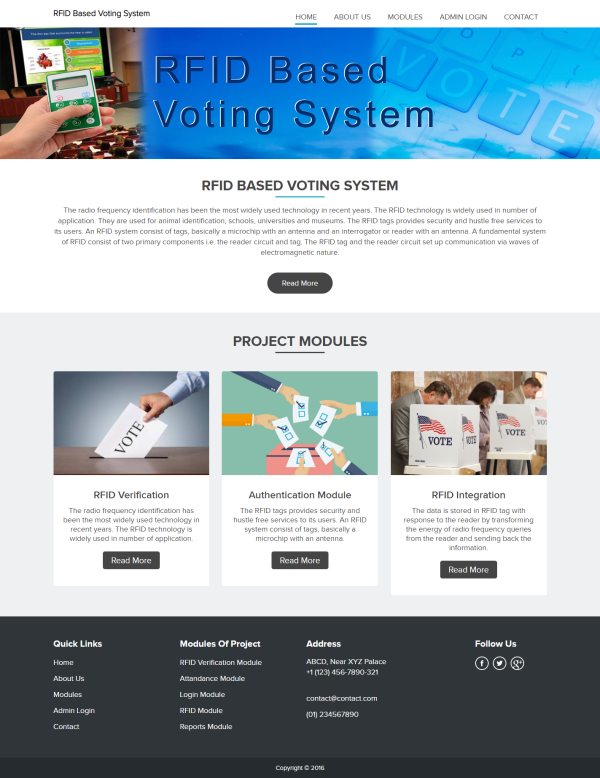
RFID Based Voting System
Political elections are often marred by fraud and scams in the voting process. To ensure a more secure election voting process, a solution known as the RFID Based Voting System has been developed. This system allows for smooth and secure conduct of elections without any disruptions. Fake voting practices by politicians can be curbed by implementing separate RFID and camera-based voter identification modules to verify the identity of voters. Let’s delve into the details of the RFID based voting system module.
The RFID based Voting System comprises a Controller kit including an Arduino UNO board, Camera, RFID Reader, LCD Display, and PC. The Arduino module serves as the control unit for the system, facilitating communication and control signals between the various modules. The Camera captures voter face detection for identification purposes, with the image processed on the PC to match voter information with their Voter ID card. Additionally, voters must swipe their RFID voter card tag on the RFID reader to validate their identity, which is displayed on the LCD screen. Once both RFID and face detection confirmations are completed, voters can cast their votes by swiping their RFID voting card tag on their preferred political party’s logo. This action confirms their vote and concludes the voting process.
The RFID based voting system helps eliminate chaos and reduce instances of fake voting by incorporating dual identification steps. This system is cost-effective compared to traditional voting systems. By adopting the RFID based voting system, real-time analysis of voting outcomes can be obtained, including information on leading candidates and their exact voter count at any given moment. This eliminates the need for manual vote counting processes and accelerates the announcement of election results.
Technology Used in the project RFID Based Voting System
Software components used in developing the user interface for the IOT RFID Based Voting System:
- Embedded C Language: Used for coding the hardware interfaces
- PHP: Business logic and web interface development
- MySQL: Database management
- Apache 2: Server for hosting the web interface
- JavaScript: Form validations and animation effects
- JQuery Library: Utilized for various functionalities such as Calendar